University of Mumbai, First Year Engineering, (Common for all Branches of Engineering) REV2019 ‘C’ Scheme
21/61
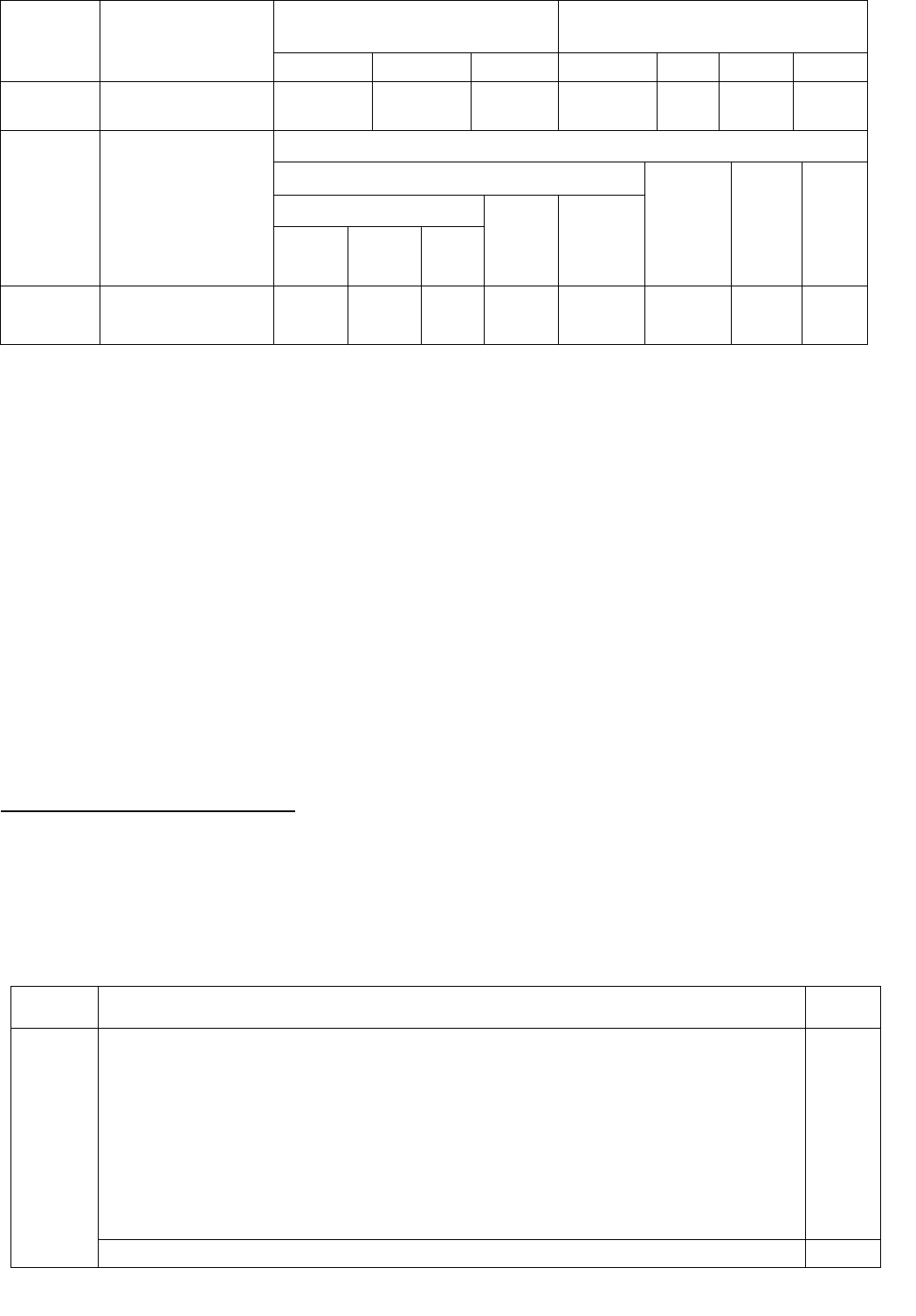
Course
Code
Course Name
Teaching Scheme
(Contact Hours)
Credits Assigned
Theory
Pract.
Tut.
Theory
Tut.
Pract.
Total
FEC104
Engineering
Mechanics
3
--
--
3
--
--
3
Course
Code
Course Name
Examination Scheme
Theory
Term
Work
Pract.
/oral
Total
Internal Assessment
End
Sem.
Exam.
Exam.
Duration
(in Hrs)
Test1
Test 2
Avg.
FEC104
Engineering
Mechanics
20
20
20
80
3
--
--
100
Objectives
1.
To familiarize the concept of equilibrium and friction
2.
To study and analyze motion of moving particles/bodies.
Outcomes: Learners will be able to…
1.
Illustrate the concept of force, moment and apply the same along with the concept of
equilibrium in two and three dimensional systems with the help of FBD.
2.
Demonstrate the understanding of Centroid and its significance and locate the same.
3.
Correlate real life application to specific type of friction and estimate required force to
overcome friction.
4.
Establish relation between velocity and acceleration of a particle and analyze the motion by
plotting the relation
5.
Illustrate different types of motions and establish Kinematic relations for a rigid body
6.
Analyze particles in motion using force and acceleration, work-energy and impulse-
momentum principles
Self-Study/pre-requisites Topics:
Resolution of a forces. Use of trigonometry functions. Parallelogram law of forces. Law of triangle.
Polygon law of forces, Lami’s theorem. Concepts of Vector Algebra.
Uniformly accelerated motion along straight line, motion under gravity, projectile motion, Time of
flight, Horizontal range, Maximum height of a projectile.
Law of conservation of Energy, Law of conservation of Momentum, Collision of Elastic Bodies.
Module
Detailed Contents
Hrs.
01
1.1 System of Coplanar Forces:
Classification of force systems, Principle of transmissibility, composition and
resolution of forces.
1.2 Resultant:
Resultant of coplanar and Non Coplanar (Space Force) force system (Concurrent
forces, parallel forces and non-concurrent Non-parallel system of forces).
Moment of force about a point, Couples, Varignon’s Theorem. Force couple
system. Distributed Forces in plane.
06
Centroid: First moment of Area, Centroid of composite plane Laminas
03

University of Mumbai, First Year Engineering, (Common for all Branches of Engineering) REV2019 ‘C’ Scheme
22/61
02
2.1 Equilibrium of System of Coplanar Forces:
Conditions of equilibrium for concurrent forces, parallel forces and non-
concurrent non- parallel general forces and Couples. Equilibrium of rigid bodies-
free body diagrams.
2.2 Equilibrium of Beams:
Types of beams, simple and compound beams, type of supports and reaction:
Determination of reactions at supports for various types of loads on beams.
(Excluding problems on internal hinges)
04
03
03
Friction:
Revision of Static Friction, Dynamic/ Kinetic Friction, Coefficient of Friction,
Angle of Friction, Laws of friction. Concept of Cone of friction.
Equilibrium of bodies on inclined plane. Application to problems involving
wedges and ladders.
04
04
Kinematics of Particle:
Motion of particle with variable acceleration. General curvilinear motion.
Tangential& Normal component of acceleration, Motion curves (a-t, v-t, s-t
curves). Application of concepts of projectile motion and related numerical.
04
05
Kinematics of Rigid Body:
Translation, Rotation and General Plane motion of Rigid body. The concept of
Instantaneous center of rotation (ICR) for the velocity. Location of ICR for 2 link
mechanism. Velocity analysis of rigid body using ICR.
03
06
6.1 Kinetics of a Particle:
Force and Acceleration: -Introduction to basic concepts, D’Alemberts Principle,
concept of Inertia force, Equations of dynamic equilibrium, Newton’s second law
of motion. (Analysis limited to simple systems only.)
04
6.2 Kinetics of a Particle: Work and Energy:
Work Energy principle for a particle in motion. Application of Work – Energy
principle to a system consists of connected masses and Springs.
04
6.3 Kinetics of a Particle: Impulse and Momentum:
Principle of linear impulse and momentum.
Impact and collision: Law of conservation of momentum, Coefficient of
Restitution. Direct Central Impact and Oblique Central Impact. Loss of Kinetic
Energy in collision of inelastic bodies.
03
Assessment:
Internal Assessment Test:
Assessment consists of two class tests of 20 marks each. The first class test is to be conducted when
approx. 40% syllabus is completed and second class test when additional 35% syllabus is
completed. Duration of each test shall be one hour.
End Semester Theory Examination:
1.
Question paper will comprise of total 06 questions, each carrying 20 marks.
2.
10 percentage of marks will be asked from the self-study topics.
3.
Total 04 questions need to be solved.
4.
Question No: 01 will be compulsory and based on entire syllabus wherein sub-questions
of 2 to 5 marks will be asked.
5.
Remaining questions will be mixed in nature.( e.g. Suppose Q.2 has part (a) from module
3 then part (b) will be from any module other than module 3 )

University of Mumbai, First Year Engineering, (Common for all Branches of Engineering) REV2019 ‘C’ Scheme
23/61
6.
In question paper weightage of each module will be proportional to number of respective
lecture hrs as mentioned in the syllabus.
References:
1.
Engineering Mechanics by R. C.Hibbeler.
2.
Engineering Mechanics by Beer &Johnston, Tata McGrawHill
3.
Engineering Mechanics by F. L. Singer, Harper& RawPublication
4.
Engineering Mechanics by Macklin & Nelson, Tata McGrawHill
5.
Engineering Mechanics by ShaumSeries
6.
Engineering Mechanics by A K Tayal, UmeshPublication.
7.
Engineering Mechanics by Kumar, Tata McGrawHill
8.
Engineering Mechanics (Statics) by Meriam and Kraige, WileyBools
9.
Engineering Mechanics (Dynamics) by Meriam and Kraige, WileyBools
University of Mumbai, First Year Engineering, (Common for all Branches of Engineering) REV2019 ‘C’ Scheme
28/61
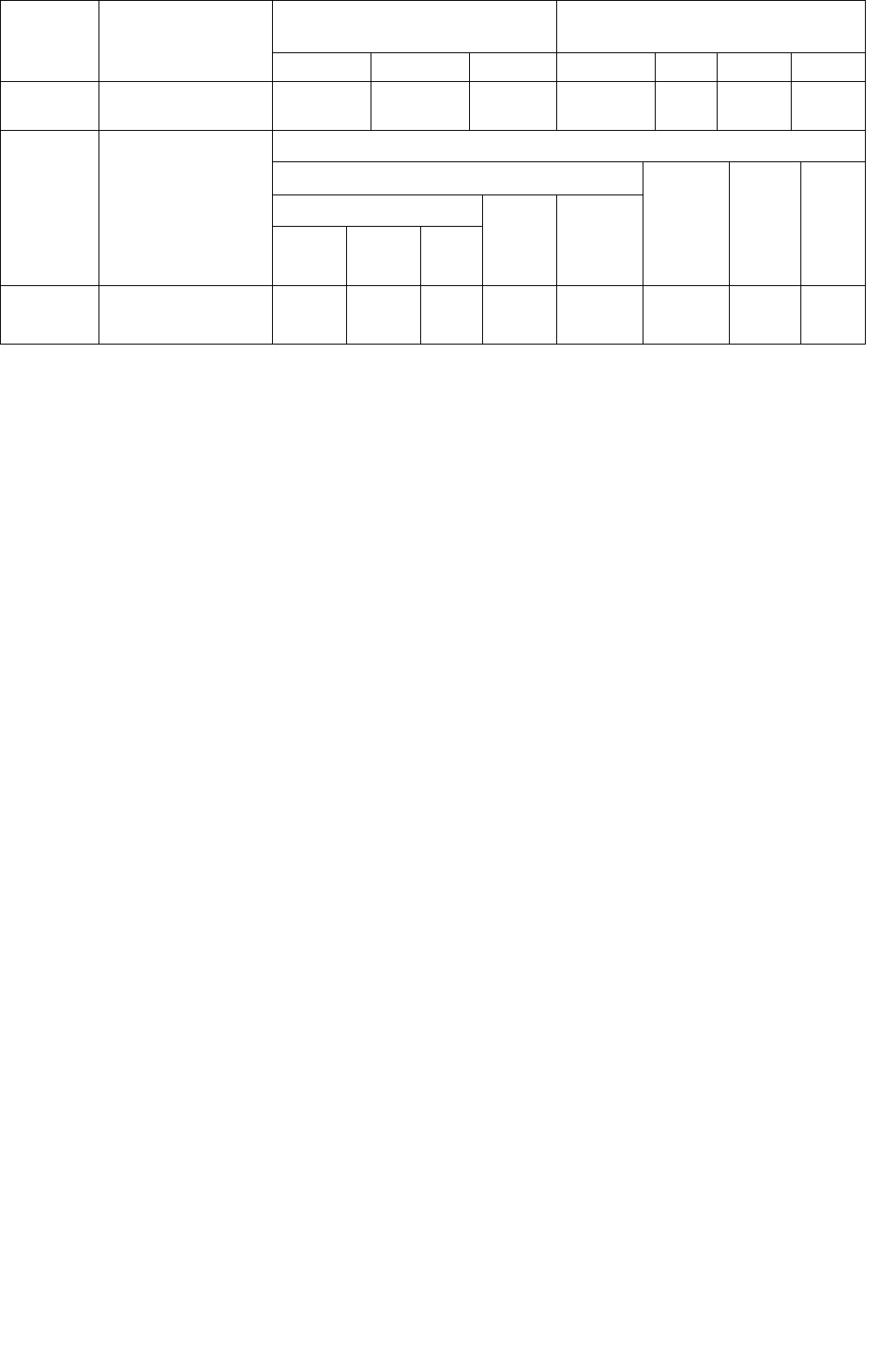
Course
Code
Course Name
Teaching Scheme
(Contact Hours)
Credits Assigned
Theory
Pract.
Tut.
Theory
Tut.
Pract.
Total
FEL103
Engineering
Mechanics
--
2
--
--
--
1
1
Course
Code
Course Name
Examination Scheme
Theory
Term
Work
Pract.
/oral
Total
Internal Assessment
End
Sem.
Exam.
Exam.
Duration
(in Hrs)
Test1
Test 2
Avg.
FEL103
Engineering
Mechanics
--
--
--
--
--
25
25
50
Objectives
1.
To acquaint the concept of equilibrium in two and three dimensional system.
2.
To study and analyse motion of moving particles/bodies.
Outcomes: Learners will be able to…
1.
Verify equations of equilibrium of coplanar force system
2.
Verify law of moments.
3.
Determine the centroid of plane lamina.
4.
Evaluate co-efficient of friction between the different surfaces in contact.
5.
Demonstrate the types of collision/impact and determine corresponding coefficient of
restitution.
6.
Differentiate the kinematics and kinetics of a particle.
List of Experiments:
Minimum six experiments from the following list of which minimum one should from
dynamics.
1.
Verification of Polygon law of coplanar forces
2.
Verification of Principle of Moments (Bell crank lever.)
3.
Determination of support reactions of a Simply Supported Beam.
4.
Determination of coefficient of friction) using inclined plane
5.
Verification of the equations of equilibrium for Non-concurrent non-parallel (General)
force system.
6.
Collision of elastic bodies (Law of conservation of momentum).
7.
Kinematics of particles. (Uniform motion of a particle, Projectile motion, motion under
gravity)
8.
Kinetics of particles. (collision of bodies)

University of Mumbai, First Year Engineering, (Common for all Branches of Engineering) REV2019 ‘C’ Scheme
29/61
Sr
No.
Assignments to be completed during Practical Session.
Minimum
Number of
Numerical
1
Resultant of Coplanar force system
4
2
Resultant of Non-Coplanar force system
3
3
Centroid of Composite plane Laminas
4
4
Equilibrium of System of Coplanar Forces
4
5
Beam Reaction
4
6
Equilibrium of bodies on inclined plane and problems involving wedges and
ladders.
4
7
Kinematics of particles (Variable acceleration + Motion Curves +Projectile
motion)
4
8
Kinetics of particles (D’Alemberts Principle, Work Energy Principle, Impulse
momentum Principle, Impact and Collisions.)
5
Assessment:
Term Work: It comprises Laboratory Experiments and Assignments.
The distribution of marks for term work shall be as follows:
Practical Work and Journal : 10 marks.
Assignments : 10 marks.
Attendance : 05 Marks
End Semester Examination:
Pair of Internal and External Examiner should conduct Oral examination based on entire
syllabus.
