Activities for
Class IX
14/04/18
12
Laboratory Manual
Mathematics is one of the most important cultural
components of every modern society. Its influence an other
cultural elements has been so fundamental and wide-spread
as to warrant the statement that her “most modern” ways
of life would hardly have been possilbly without mathematics.
Appeal to such obvious examples as electronics radio,
television, computing machines, and space travel, to
substantiate this statement is unnecessary : the elementary
art of calculating is evidence enough. Imagine trying to get
through three day without using numbers in some fashion
or other!
– R.L. Wilder
14/04/18
Mathematics 13
METHOD OF CONSTRUCTION
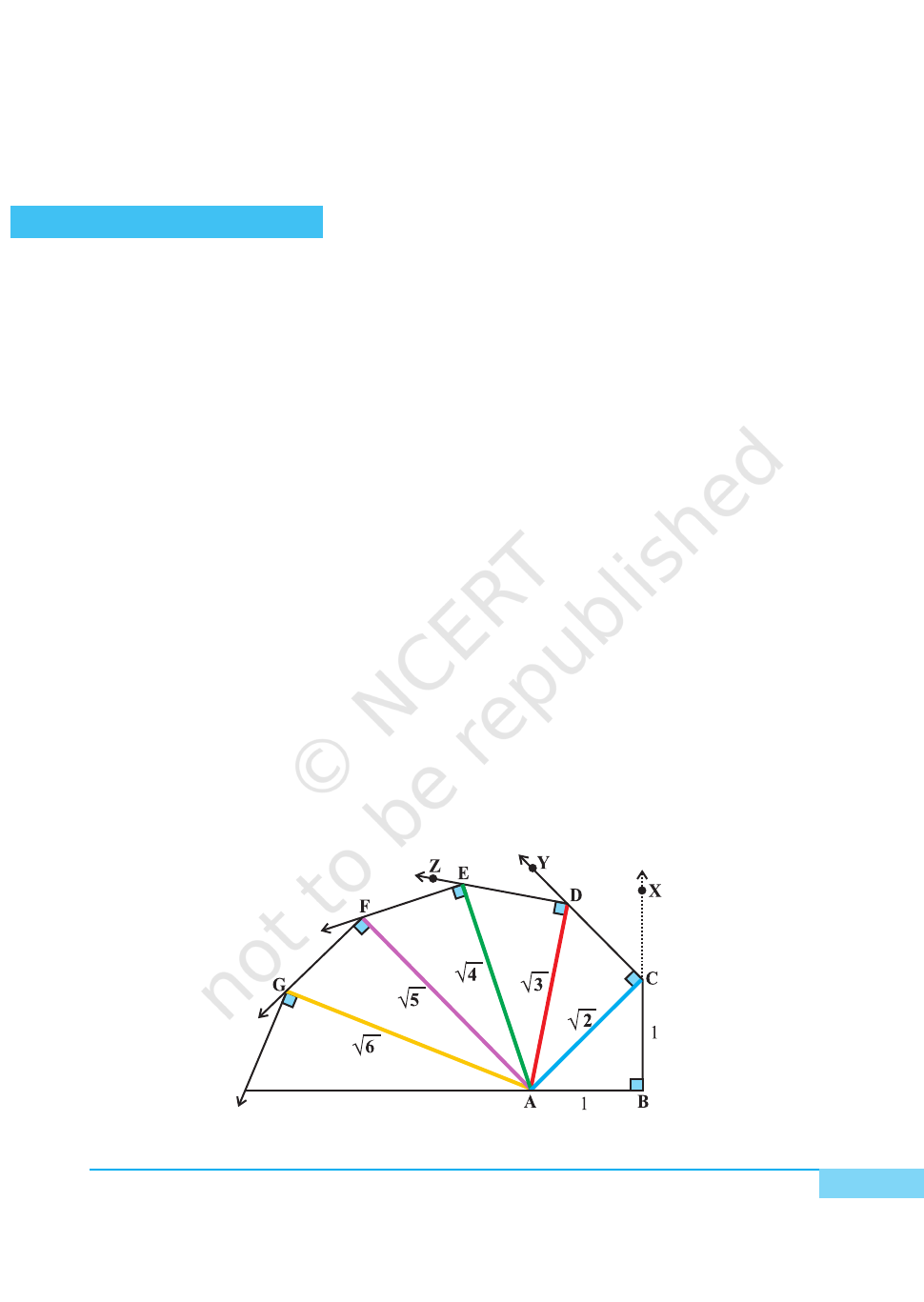
1. Take a piece of plywood with dimensions 30 cm × 30 cm.
2. Taking 2 cm = 1 unit, draw a line segment AB of length one unit.
3. Construct a perpendicular BX at the line segment AB using set squares (or
compasses).
4. From BX, cut off BC = 1 unit. Join AC.
5. Using blue coloured thread (of length equal to AC) and adhesive, fix the
thread along AC.
6. With AC as base and using set squares (or compasses), draw CY perpendicular
to AC.
7. From CY, cut-off CD = 1 unit and join AD.
OBJECTIVE
MATERIAL REQUIRED
To construct a square-root spiral.
Coloured threads, adhesive,
drawing pins, nails, geometry box,
sketch pens, marker, a piece of
plywood.
Fig. 1
Activity 1
Mathematics 13
14/04/18

14
Laboratory Manual
8. Fix orange coloured thread (of length equal to AD) along AD with adhesive.
9. With AD as base and using set squares (or compasses), draw DZ
perpendicular to AD.
10. From DZ, cut off DE = 1 unit and join AE.
11. Fix green coloured thread (of length equal to AE) along AE with adhesive
[see Fig. 1].
Repeat the above process for a sufficient number of times. This is called “a
square root spiral”.
DEMONSTRATION
1. From the figure, AC
2
= AB
2
+ BC
2
= 12 + 12 = 2 or AC =
2
.
AD
2
= AC
2
+ CD
2
= 2 + 1 = 3 or AD =
3
.
2. Similarly, we get the other lengths AE, AF, AG, ... as
4
or 2,
5
,
6
....
OBSERVATION
On actual measurement
AC = ..... , AD = ...... , AE = ...... , AF =....... , AG = ......
2
= AC = ............... (approx.),
3
= AD = ............... (approx.),
4
= AE = ............... (approx.),
5
= AF = ............... (approx.)
APPLICATION
Through this activity, existence of irrational numbers can be illustrated.
14/04/18
Mathematics 15
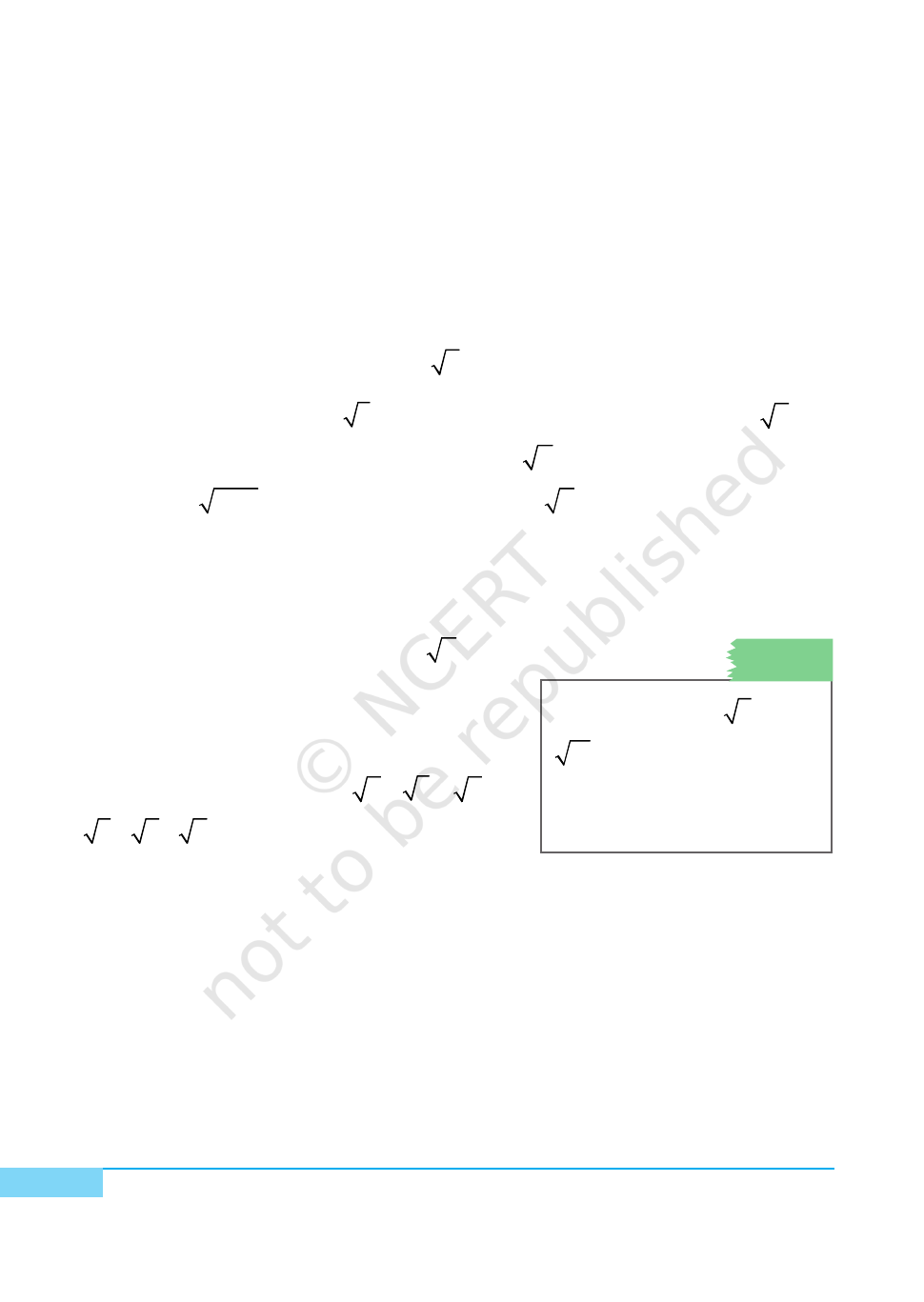
METHOD OF CONSTRUCTION
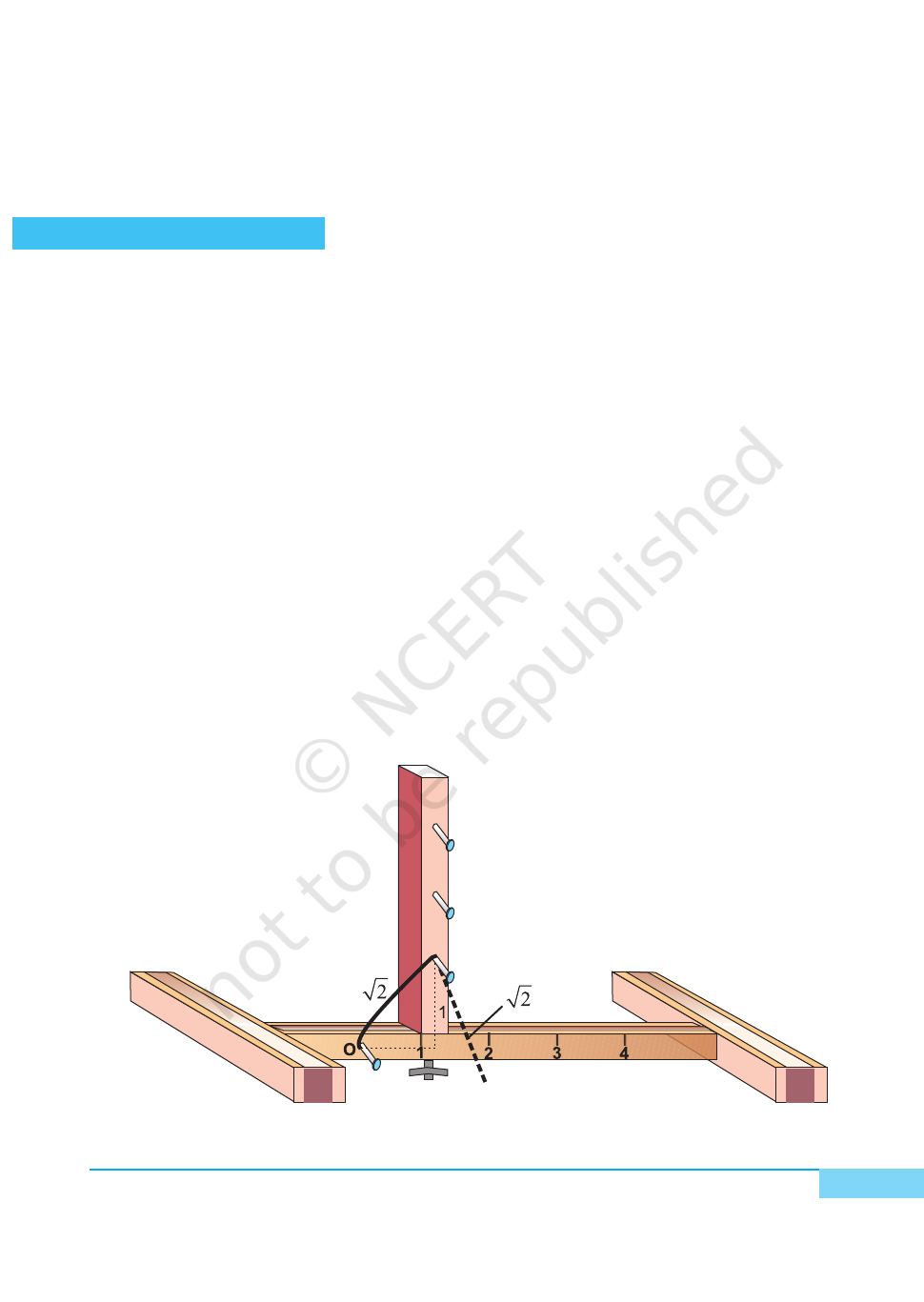
1. Make a straight slit on the top of one of the wooden strips. Fix another
wooden strip on the slit perpendicular to the former strip with a screw at
the bottom so that it can move freely along the slit [see Fig.1].
2. Paste one photocopy of the scale on each of these two strips as shown in
Fig. 1.
3. Fix nails at a distance of 1 unit each, starting from 0, on both the strips as
shown in the figure.
4. Tie a thread at the nail at 0 on the horizontal strip.
OBJECTIVE
MATERIAL REQUIRED
To represent some irrational numbers
on the number line.
Two cuboidal wooden strips,
thread, nails, hammer, two photo
copies of a scale, a screw with nut,
glue, cutter.
Activity 2
Fig. 1
14/04/18
16
Laboratory Manual
DEMONSTRATION
1. Take 1 unit on the horizontal scale and fix the perpendicular wooden strip
at 1 by the screw at the bottom.
2. Tie the other end of the thread to unit ‘1’ on the perpendicular strip.
3. Remove the thread from unit ‘1’ on the perpendicular strip and place it on
the horizontal strip to represent
2
on the horizontal strip [see Fig. 1].
Similarly, to represent
3
, fix the perpendicular wooden strip at
2
and
repeat the process as above. To represent
a
, a > 1, fix the perpendicular
scale at
–1
a
and proceed as above to get
a
.
OBSERVATION
On actual measurement:
a – 1 = ...........
a
= ...........
APPLICATION
The activity may help in representing some
irrational numbers such as
2
,
3
,
4
,
5
,
6
,
7
, .... on the number line.
NOTE
You may also find
a
such as
13
by fixing the perpendicular
strip at 3 on the horizontal strip
and tying the other end of thread
at 2 on the vertical strip.
14/04/18
Mathematics 17
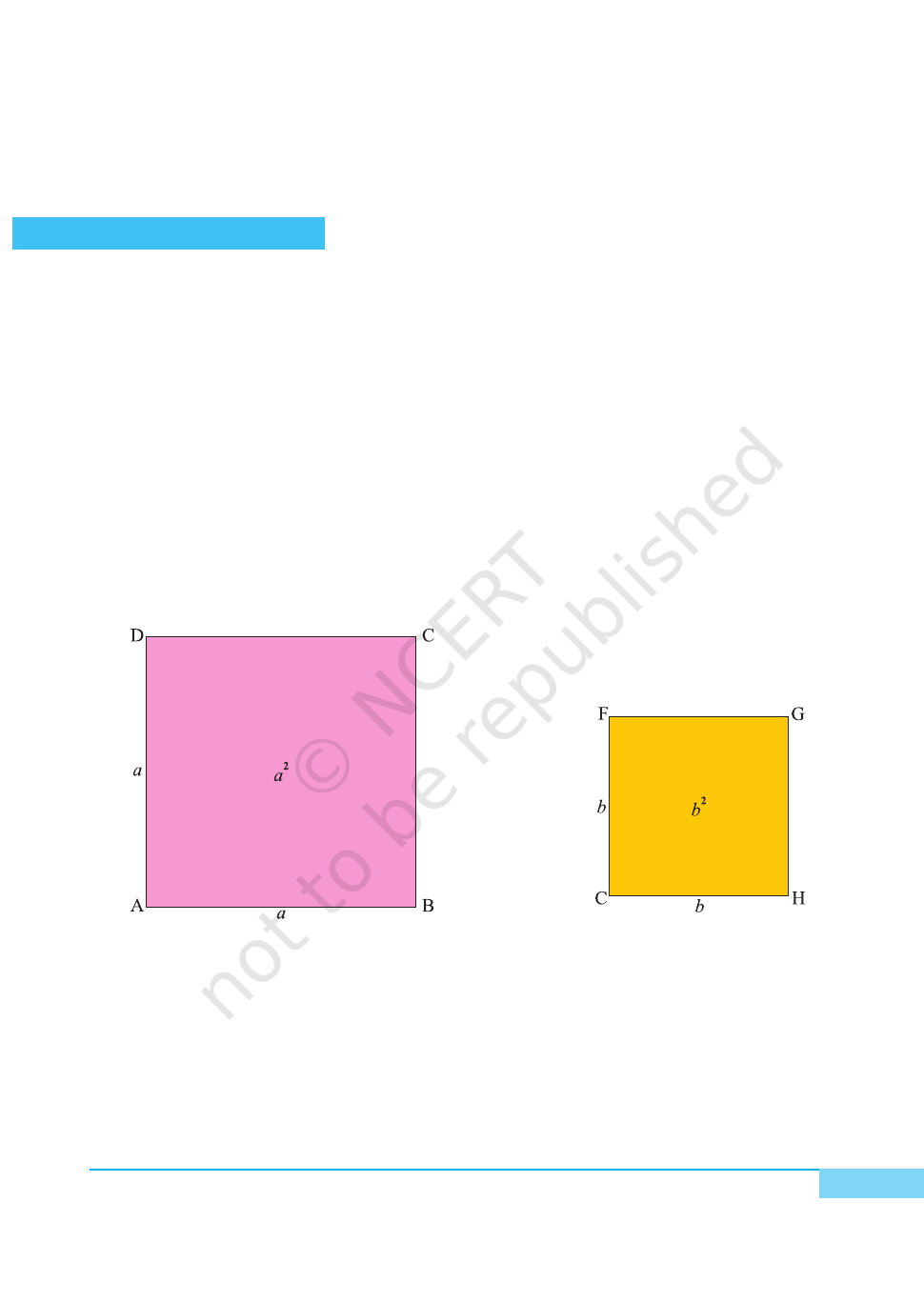
METHOD OF CONSTRUCTION
1. Cut out a square of side length a units from a drawing sheet/cardboard and
name it as square ABCD [see Fig. 1].
2. Cut out another square of length b units from a drawing sheet/cardboard and
name it as square CHGF [see Fig. 2].
OBJECTIVE
MATERIAL REQUIRED
To verify the algebraic identity :
(a + b)
2
= a
2
+ 2ab + b
2
Drawing sheet, cardboard, cello-
tape, coloured papers, cutter and
ruler.
Activity 3
Fig. 1
Fig. 2
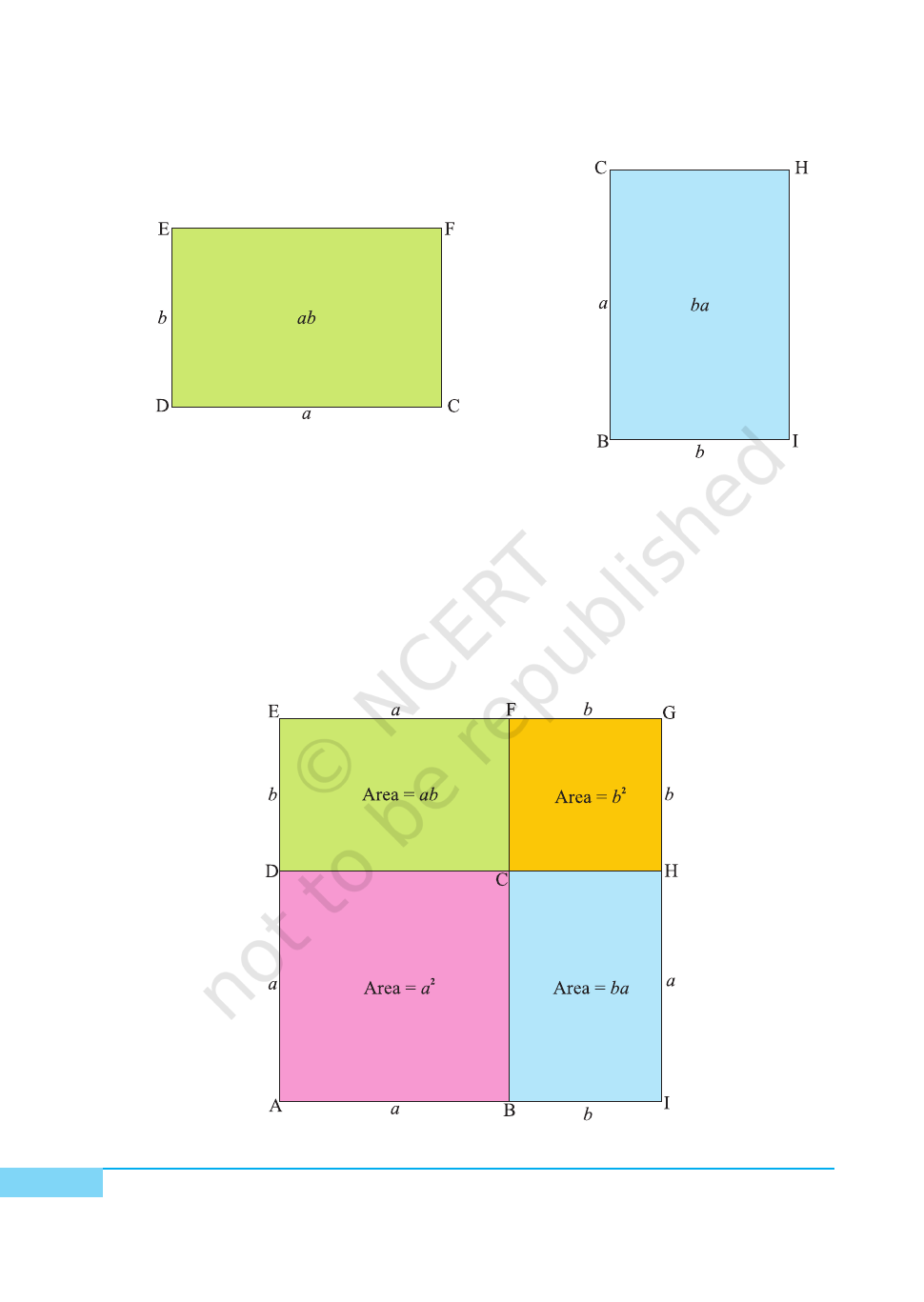
3. Cut out a rectangle of length a units and breadth b units from a drawing
sheet/cardbaord and name it as a rectangle DCFE [see Fig. 3].
4. Cut out another rectangle of length b units and breadth a units from a drawing
sheet/cardboard and name it as a rectangle BIHC [see Fig. 4].
14/04/18
18
Laboratory Manual
5. Total area of these four cut-out figures
= Area of square ABCD + Area of square CHGF + Area of rectangle DCFE
+ Area of rectangle BIHC
= a
2
+ b
2
+ ab + ba = a
2
+ b
2
+ 2ab.
6. Join the four quadrilaterals using cello-tape as shown in Fig. 5.
Fig. 3
Fig. 4
Fig. 5
14/04/18

Mathematics 19
Clearly, AIGE is a square of side (a + b). Therefore, its area is (a + b)
2
. The
combined area of the constituent units = a
2
+ b
2
+ ab + ab = a
2
+ b
2
+ 2ab.
Hence, the algebraic identity (a + b)
2
= a
2
+ 2ab + b
2
Here, area is in square units.
OBSERVATION
On actual measurement:
a = .............., b = .............. (a+b) = ..............,
So, a
2
=
.............. b
2
= .............., ab = ..............
(a+b)
2
= .............., 2ab = ..............
Therefore, (a+b)
2
= a
2
+ 2ab + b
2
.
The identity may be verified by taking different values of a and b.
APPLICATION
The identity may be used for
1. calculating the square of a number expressed as the sum of two convenient
numbers.
2. simplifications/factorisation of some algebraic expressions.
14/04/18
20
Laboratory Manual
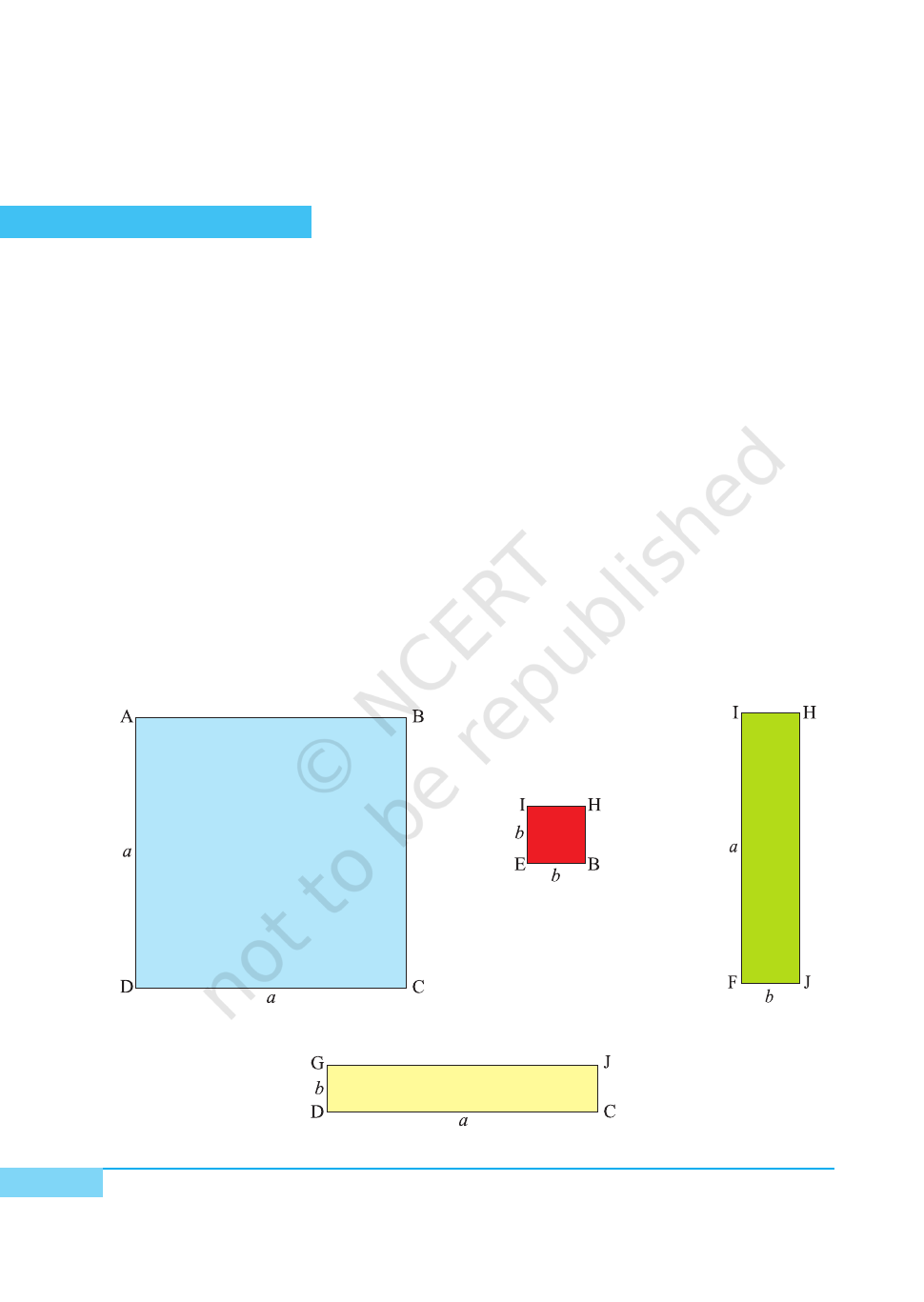
METHOD OF CONSTRUCTION
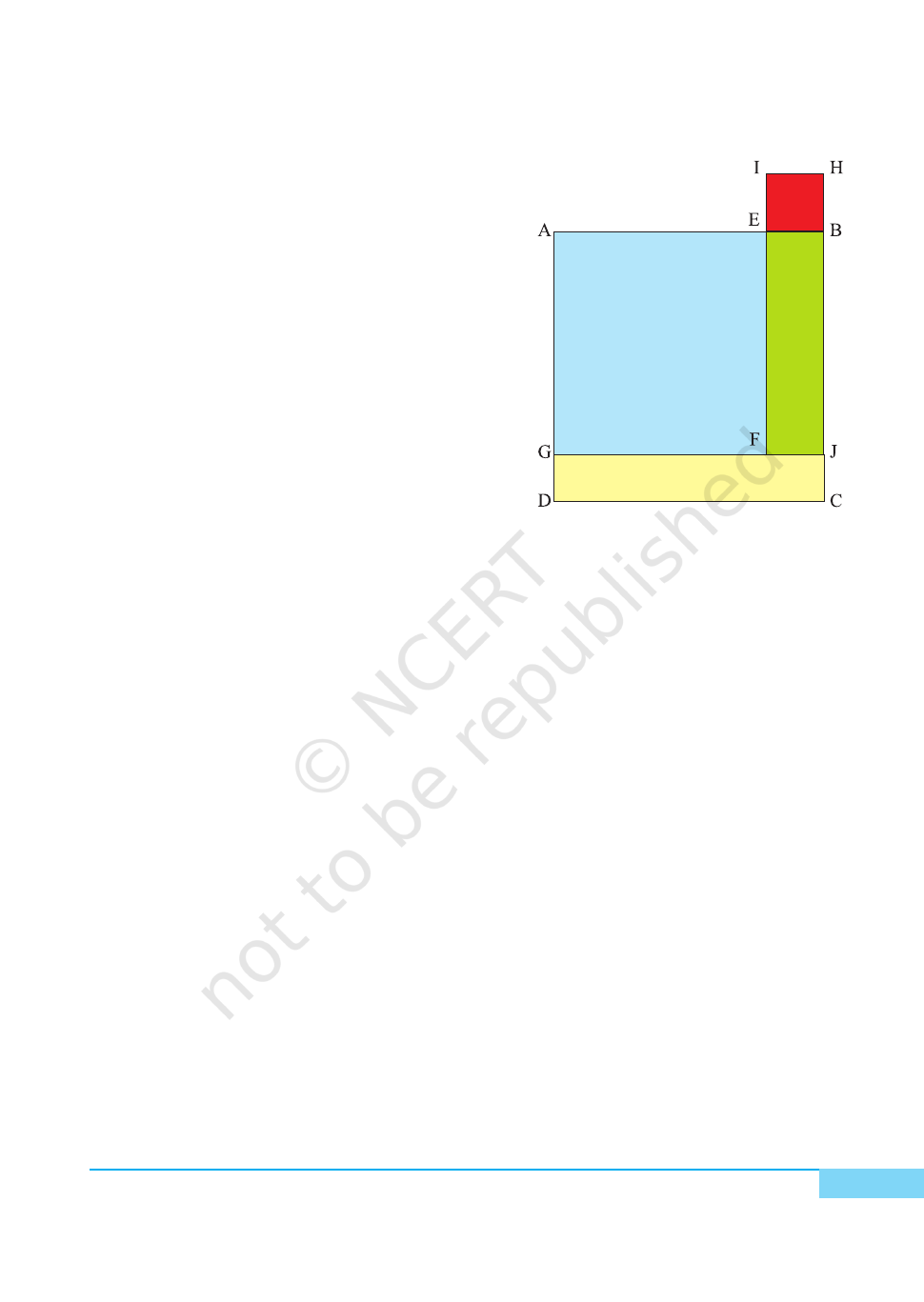
1. Cut out a square ABCD of side a units from a drawing sheet/cardboard [see Fig. 1].
2. Cut out a square EBHI of side b units (b < a) from a drawing sheet/cardboard
[see Fig. 2].
3. Cut out a rectangle GDCJ of length a units and breadth b units from a drawing
sheet/cardboard [see Fig. 3].
4. Cut out a rectangle IFJH of length a units and breadth b units from a drawing
sheet/cardboard [see Fig. 4].
OBJECTIVE
MATERIAL REQUIRED
To verify the algebraic identity :
(a – b)
2
= a
2
– 2ab + b
2
Drawing sheets, cardboard,
coloured papers, scissors, ruler and
adhesive.
Activity 4
Fig. 1
Fig. 2
Fig. 3
Fig. 4
14/04/18
Mathematics 21
5. Arrange these cut outs as shown in Fig. 5.
DEMONSTRATION
According to figure 1, 2, 3, and 4, Area of
square ABCD = a
2
, Area of square EBHI = b
2
Area of rectangle GDCJ = ab, Area of
rectangle IFJH = ab
From Fig. 5, area of square AGFE = AG × GF
= (a – b) (a – b) = (a – b)
2
Now, area of square AGFE = Area of square
ABCD + Area of square EBHI
– Area of rectangle IFJH – Area of rectangle
GDCJ
= a
2
+ b
2
– ab – ab
= a
2
– 2ab + b
2
Here, area is in square units.
OBSERVATION
On actual measurement:
a = .............., b = .............., (a – b) = ..............,
So, a
2
=
.............., b
2
= .............., (a – b)
2
= ..............,
ab = .............., 2ab = ..............
Therefore, (a – b)
2
= a
2
– 2ab + b
2
APPLICATION
The identity may be used for
1. calculating the square of a number expressed as a difference of two
convenient numbers.
2. simplifying/factorisation of some algebraic expressions.
Fig. 5
14/04/18

22
Laboratory Manual
METHOD OF CONSTRUCTION
1. Take a cardboard of a convenient size and paste a coloured paper on it.
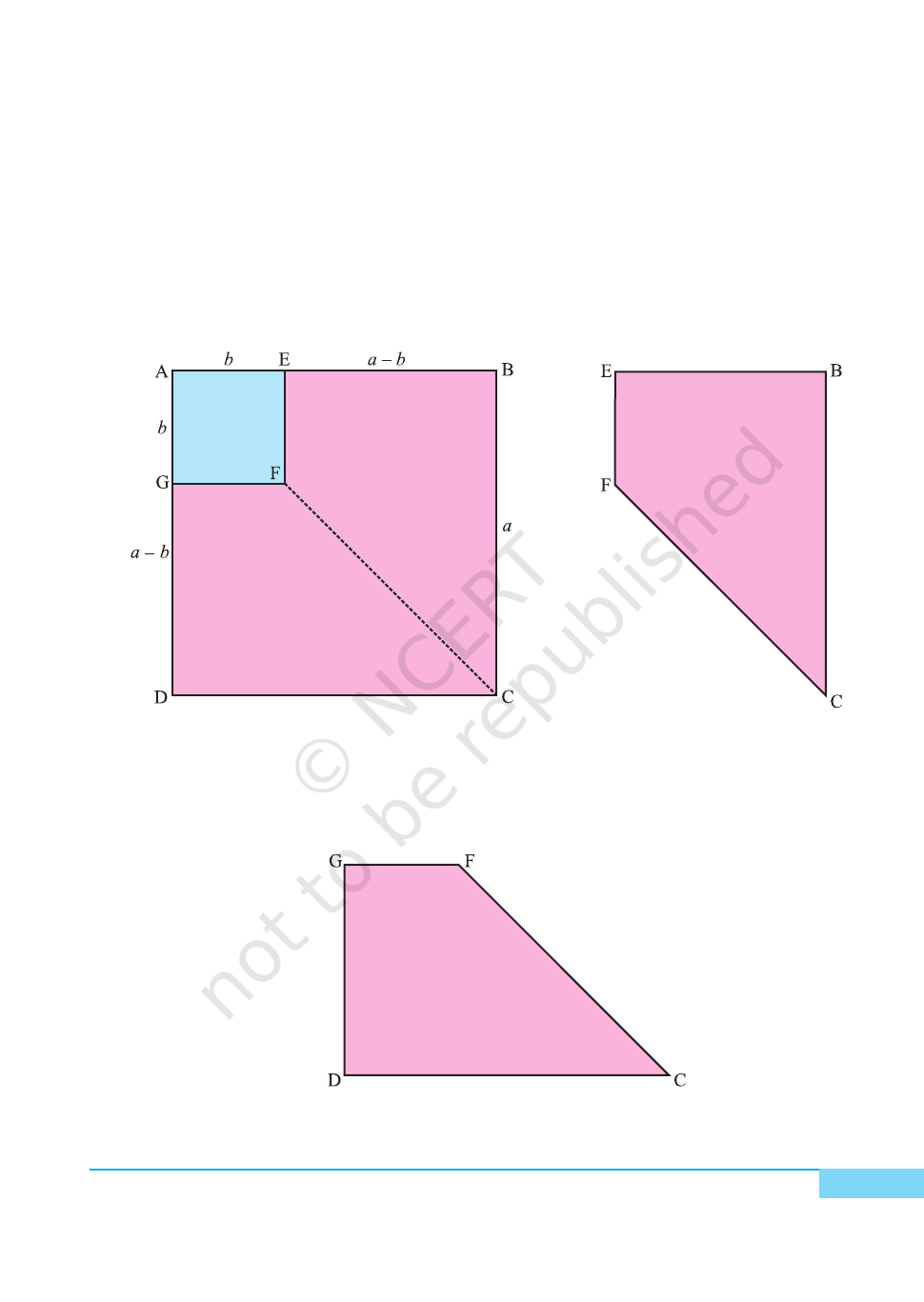
2. Cut out one square ABCD of side a units from a drawing sheet [see Fig. 1].
3. Cut out one square AEFG of side b units (b < a) from another drawing sheet
[see Fig. 2].
OBJECTIVE
MATERIAL REQUIRED
To verify the algebraic identity :
a
2
– b
2
= (a + b)(a – b)
Drawing sheets, cardboard,
coloured papers, scissors, sketch
pen, ruler, transparent sheet and
adhesive.
Activity 5
Fig. 1
Fig. 2
14/04/18
Mathematics 23
4. Arrange these squares as shown in Fig. 3.
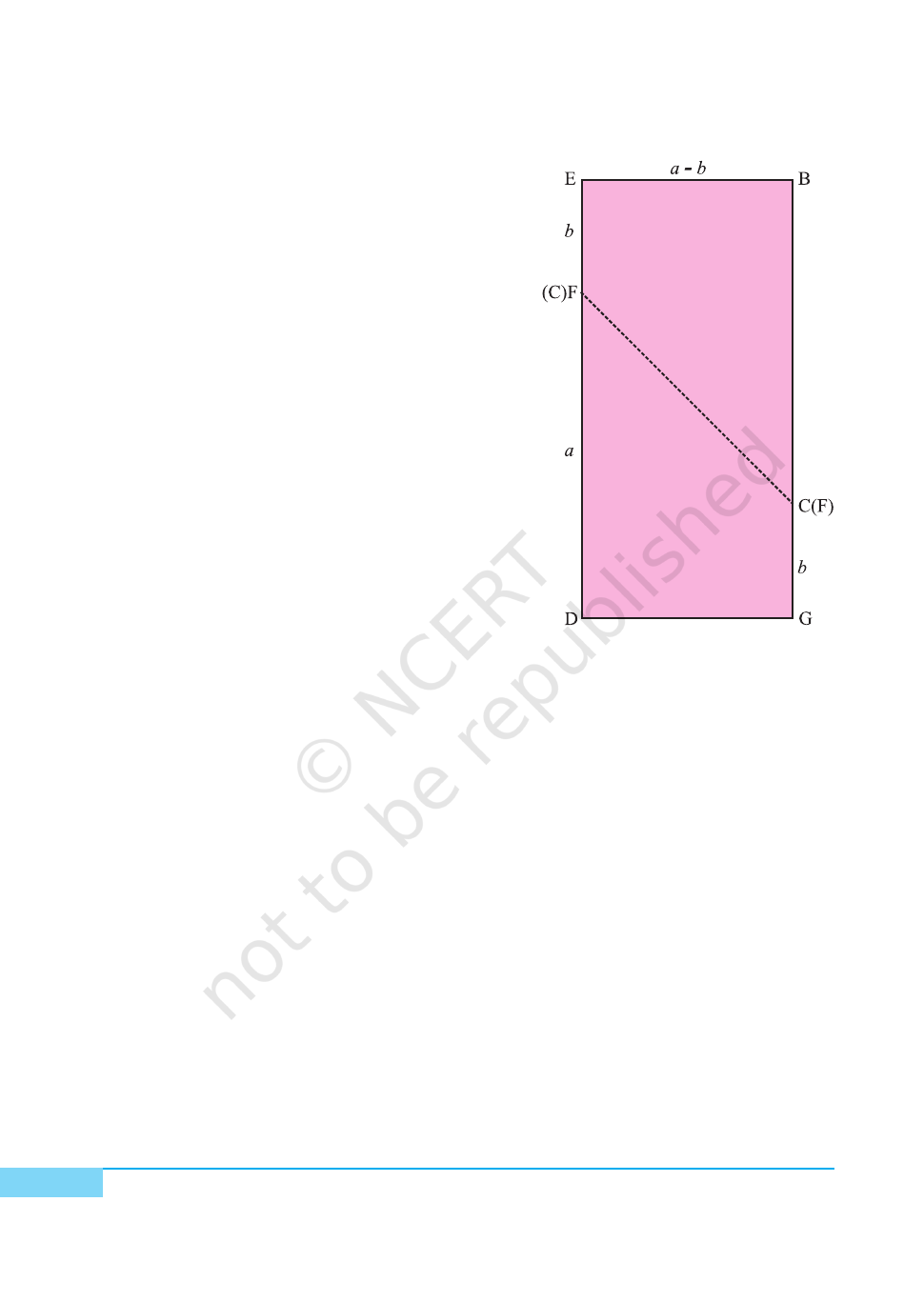
5. Join F to C using sketch pen. Cut out trapeziums congruent to EBCF and
GFCD using a transparent sheet and name them as EBCF and GFCD,
respectively [see Fig. 4 and Fig. 5].
Fig. 3
Fig. 4
Fig. 5
14/04/18
24
Laboratory Manual
6. Arrange these trapeziums as shown in
Fig. 6.
DEMONSTRATION
Area of square ABCD = a
2
Area of square AEFG = b
2
In Fig. 3,
Area of square ABCD – Area of square
AEFG
= Area of trapezium EBCF + Area of
trapezium GFCD
= Area of rectangle EBGD [Fig. 6].
= ED × DG
Thus, a
2
– b
2
= (a+b) (a–b)
Here, area is in square units.
OBSERVATION
On actual measurement:
a = .............., b = .............., (a+b) = ..............,
So, a
2
=
.............., b
2
= .............., (a–b) = ..............,
a
2
–b
2
= .............., (a+b) (a–b) = ..............,
Therefore, a
2
–b
2
= (a+b) (a–b)
APPLICATION
The identity may be used for
1. difference of two squares
2. some products involving two numbers
3. simplification and factorisation of algebraic expressions.
Fig. 6
14/04/18
Mathematics 25
METHOD OF CONSTRUCTION
1. Take a hardboard of a convenient size and paste a white paper on it.
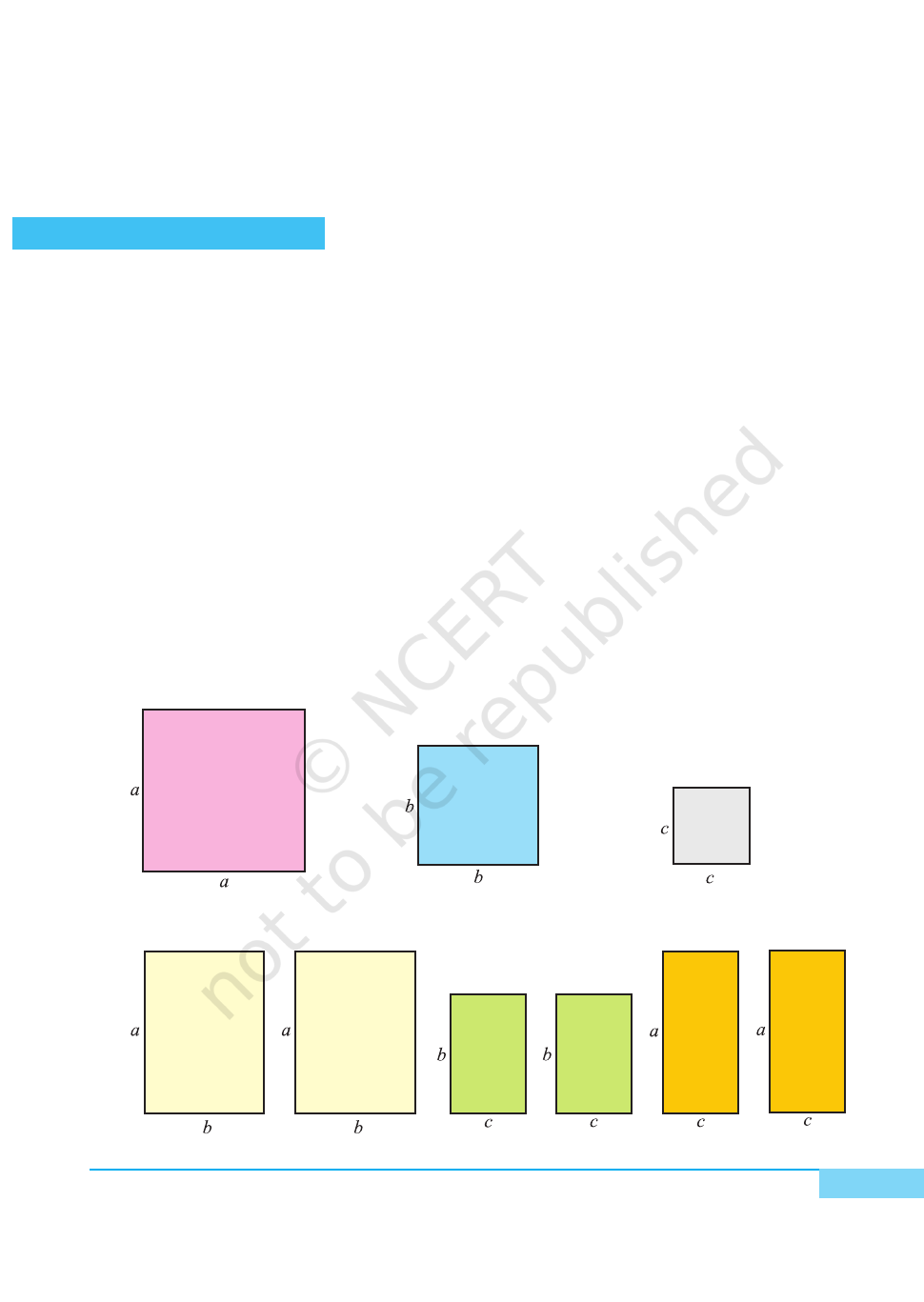
2. Cut out a square of side a units from a coloured paper [see Fig. 1].
3. Cut out a square of side b units from a coloured paper [see Fig. 2].
4. Cut out a square of side c units from a coloured paper [see Fig. 3].
5. Cut out two rectangles of dimensions a× b, two rectangles of dimensions
b × c and two rectangles of dimensions c × a square units from a coloured
paper [see Fig. 4].
OBJECTIVE
MATERIAL REQUIRED
To verify the algebraic identity :
(a+b+c)
2
= a
2
+ b
2
+ c
2
+ 2ab + 2bc + 2ca
Hardboard, adhesive, coloured
papers, white paper.
Activity 6
Fig. 1
Fig. 4
Fig. 2 Fig. 3
14/04/18
26
Laboratory Manual
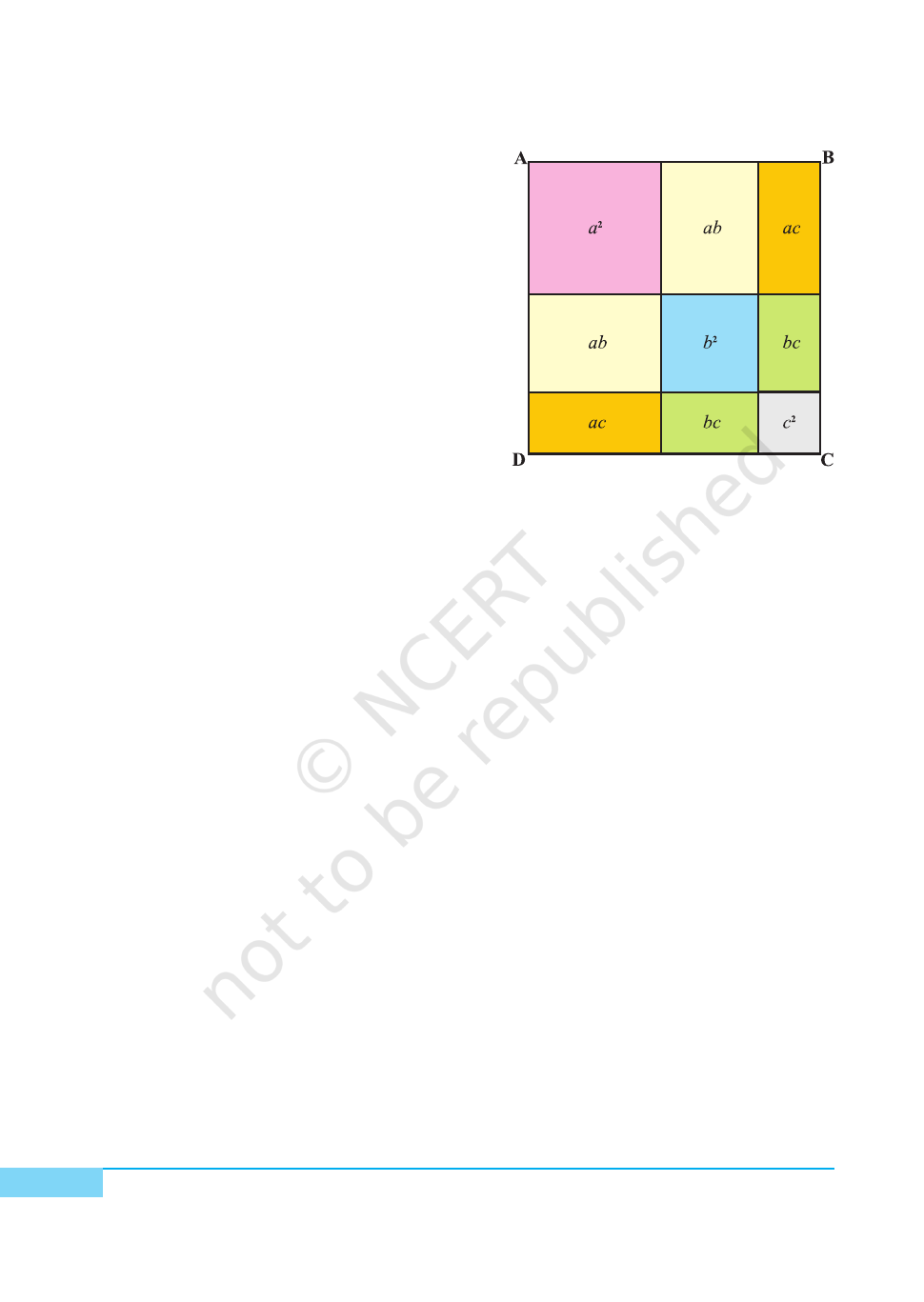
6. Arrange the squares and rectangles on
the hardboard as shown in Fig. 5.
DEMONSTRATION
From the arrangement of squares and
rectangles in Fig. 5, a square ABCD is
obtained whose side is (a+b+c) units.
Area of square ABCD = (a+b+c)
2
.
Therefore, (a+b+c)
2
= sum of all the
squares and rectangles shown in Fig. 1 to
Fig. 4.
= a
2
+ ab + ac + ab + b
2
+ bc + ac + bc + c
2
= a
2
+ b
2
+ c
2
+ 2ab + 2bc + 2ca
Here, area is in square units.
OBSERVATION
On actual measurement:
a = .............., b = .............., c = ..............,
So, a
2
=
.............., b
2
= .............., c
2
= .............., ab= ..............,
bc= .............., ca = .............., 2ab = .............., 2bc = ..............,
2ca= .............., a+b+c = .............., (a+b+c)
2
= ..............,
Therefore, (a+b+c)
2
= a
2
+ b
2
+c
2
+2ab + 2bc + 2ca
APPLICATION
The identity may be used for
1. simiplification/factorisation of algebraic expressions
2. calculating the square of a number expressed as a sum of three convenient
numbers.
Fig. 5
14/04/18
Mathematics 27
METHOD OF CONSTRUCTION
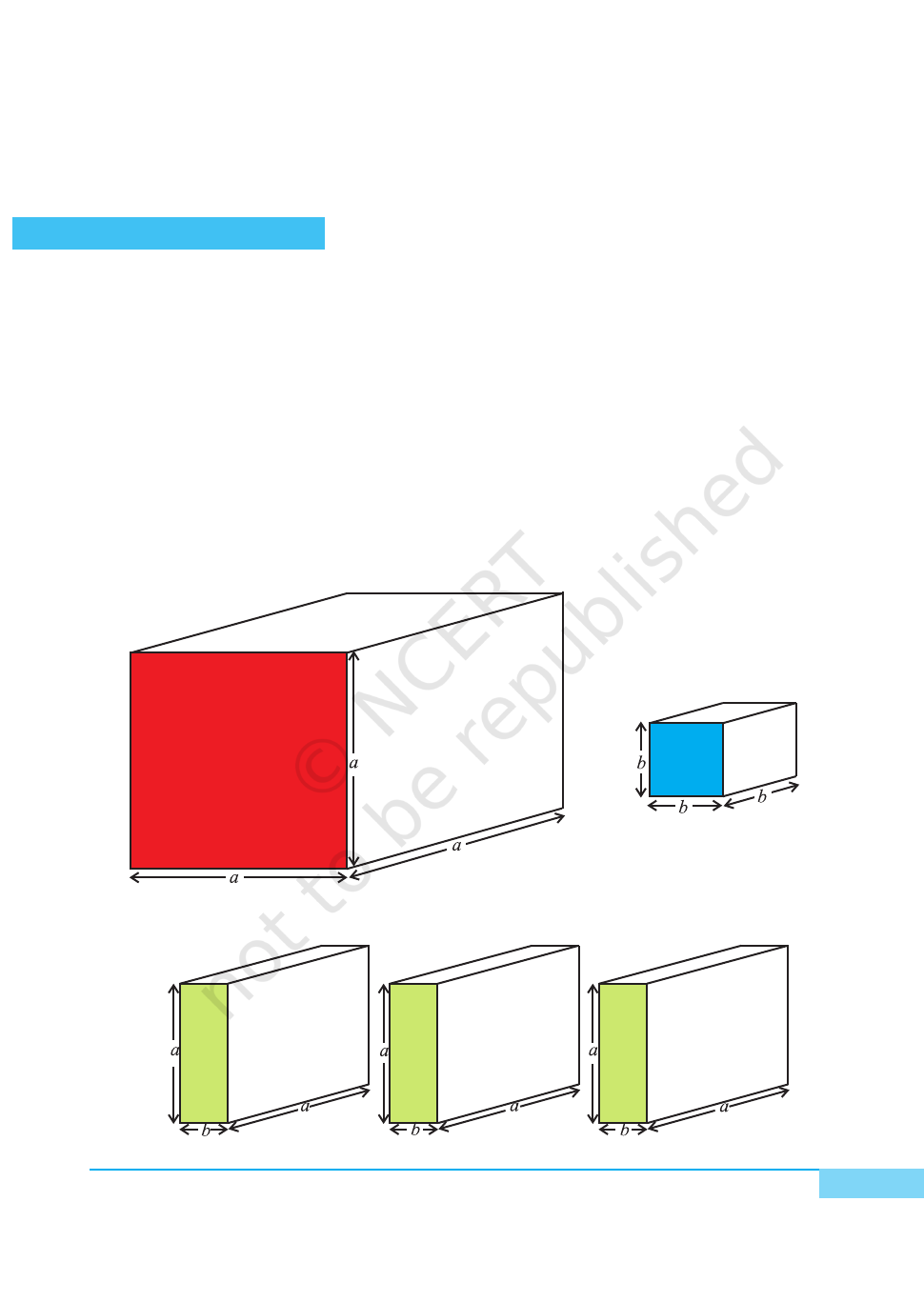
1. Make a cube of side a units and one more cube of side b units (b < a), using
acrylic sheet and cello-tape/adhesive [see Fig. 1 and Fig. 2].
2. Similarly, make three cuboids of dimensions a×a×b and three cuboids of
dimensions a×b×b [see Fig. 3 and Fig. 4].
OBJECTIVE
MATERIAL REQUIRED
To verify the algebraic identity :
(a+b)
3
= a
3
+ b
3
+ 3a
2
b + 3ab
2
Acrylic sheet, coloured papers,
glazed papers, saw, sketch pen,
adhesive, Cello-tape.
Activity 7
Fig. 1
Fig. 2
Fig. 3
14/04/18
28
Laboratory Manual
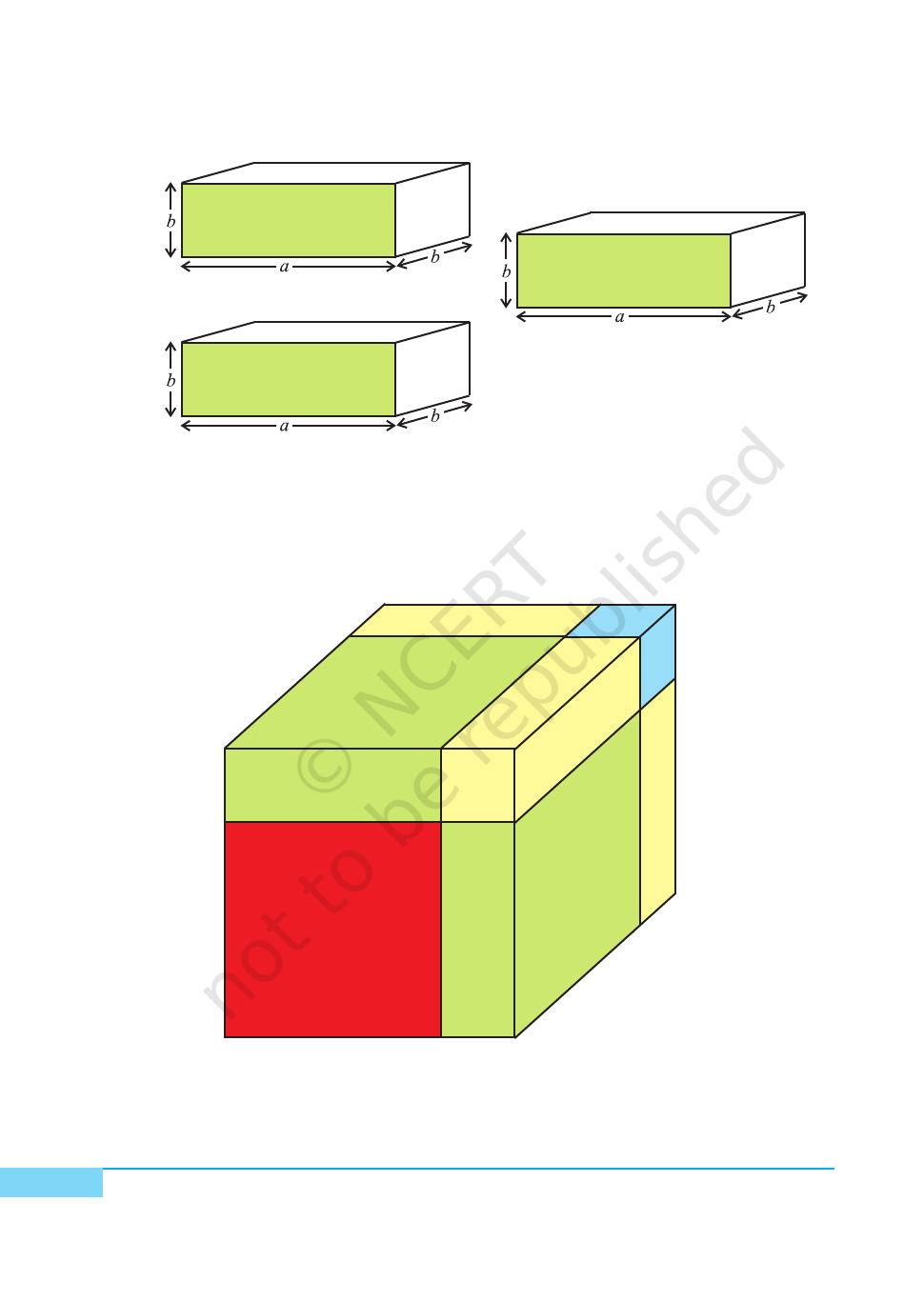
3. Arrange the cubes and cuboids as shown in Fig. 5.
Fig. 4
Fig. 5
14/04/18

Mathematics 29
DEMONSTRATION
Volume of the cube of side a = a×a×a = a
3
, volume of the cube of side b = b
3
Volume of the cuboid of dimensions a×a×b = a
2
b, volume of three such cuboids
= 3a
2
b
Volume of the cuboid of dimensions a×b×b = ab
2
, volume of three such cuboids
= 3ab
2
Solid figure obtained in Fig. 5 is a cube of side (a + b)
Its volume = (a + b)
3
Therefore, (a+b)
3
= a
3
+ b
3
+ 3a
2
b + 3ab
2
Here, volume is in cubic units.
OBSERVATION
On actual measurement:
a = .............., b = ............., a
3
= ..............,
So, a
3
=
.............., b
3
= ............., a
2
b
= .............., 3a
2
b= ..............,
ab
2
= .............., 3ab
2
= .............., (a+b)
3
= ..............,
Therefore, (a+b)
3
= a
3
+ b
3
+3a
2
b + 3ab
2
APPLICATION
The identity may be used for
1. calculating cube of a number expressed as the sum of two convenient
numbers
2. simplification and factorisation of algebraic expressions.
14/04/18

30
Laboratory Manual
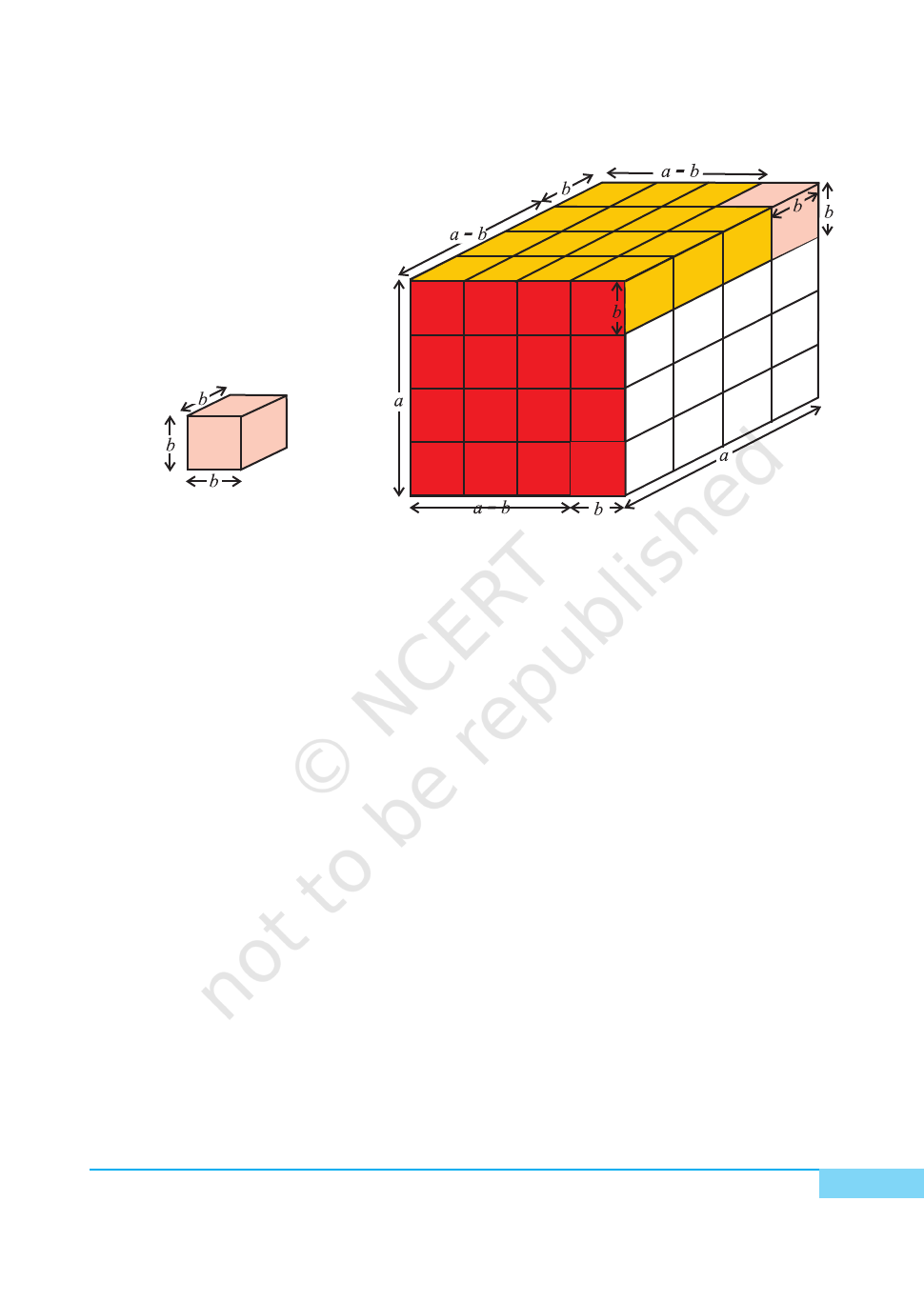
METHOD OF CONSTRUCTION
1. Make a cube of side (a – b) units (a > b)using acrylic sheet and cellotape/
adhesive [see Fig. 1].
2. Make three cuboids each of dimensions (a–b) × a × b and one cube of side
b units using acrylic sheet and cellotape [see Fig. 2 and Fig. 3].
3. Arrange the cubes and cuboids as shown in Fig. 4.
OBJECTIVE
MATERIAL REQUIRED
To verify the algebraic identity
(a – b)
3
= a
3
– b
3
– 3(a – b)ab
Acrylic sheet, coloured papers,
saw, sketch pens, adhesive, Cello-
tape.
Activity 8
Fig. 1
Fig. 2
14/04/18
Mathematics 31
Fig. 3 Fig. 4
DEMONSTRATION
Volume of the cube of side (a – b) units in Fig. 1 = (a– b)
3
Volume of a cuboid in Fig. 2 = (a–b) ab
Volume of three cuboids in Fig. 2 = 3 (a–b) ab
Volume of the cube of side b in Fig. 3 = b
3
Volume of the solid in Fig. 4 = (a–b)
3
+ (a–b) ab + (a–b) ab + (a – b) ab + b
3
= (a–b)
3
+ 3(a–b) ab + b
3
(1)
Also, the solid obtained in Fig. 4 is a cube of side a
Therefore, its volume = a
3
(2)
From (1) and (2),
(a–b)
3
+ 3(a–b) ab + b
3
= a
3
or (a–b)
3
= a
3
– b
3
– 3ab (a–b).
Here, volume is in cubic units.
14/04/18

32
Laboratory Manual
OBSERVATION
On actual measurement:
a = .............., b = .............., a–b = ..............,
So, a
3
=
.............., ab
= ..............,
b
3
= .............., ab(a–b) = ..............,
3ab (a–b)
= .............., (a–b)
3
= ..............,
Therefore, (a–b)
3
= a
3
– b
3
– 3ab(a–b)
APPLICATION
The identity may be used for
1. calculating cube of a number
expressed as a difference of two
convenient numbers
2. simplification and factorisation of
algebraic expressions.
NOTE
This identity can also be
expressed as :
(a – b)
3
= a
3
– 3a
2
b + 3ab
2
– b
3
.
14/04/18
Mathematics 33
METHOD OF CONSTRUCTION
1. Make a cube of side a units and another cube of side b units as shown in
Fig. 1 and Fig. 2 by using acrylic sheet and cellotape/adhesive.
2. Make a cuboid of dimensions a × a × b [see Fig. 3].
3. Make a cuboid of dimensions a × b × b [see Fig. 4].
4. Arrange these cubes and cuboids as shown in Fig. 5.
OBJECTIVE
MATERIAL REQUIRED
To verify the algebraic identity :
a
3
+ b
3
= (a + b) (a
2
– ab + b
2
)
Acrylic sheet, glazed papers, saw,
adhesive, cellotape, coloured
papers, sketch pen, etc.
Activity 9
Fig. 1
Fig. 2
Fig. 3
Fig. 4
Fig. 5
14/04/18
34
Laboratory Manual
DEMONSTRATION
Volume of cube in Fig. 1 = a
3
Volume of cube in Fig. 2 = b
3
Volume of cuboid in Fig. 3 = a
2
b
Volume of cuboid in Fig. 4 = ab
2
Volume of solid in Fig. 5 = a
3
+b
3
+
a
2
b + ab
2
= (a+b) (a
2
+ b
2
)
Removing cuboids of volumes a
2
b and ab
2
, i.e.,
ab (a + b) from solid obtained in Fig. 5, we
get the solid in Fig. 6.
Volume of solid in Fig. 6 = a
3
+ b
3
.
Therefore, a
3
+ b
3
= (a+b) (a
2
+ b
2
) – ab (a + b)
= (a+b) (a
2
+ b
2
– ab)
Here, volumes are in cubic units.
OBSERVATION
On actual measurement:
a = .............., b = ..............,
So, a
3
=
.............., b
3
= .............., (a+b) = .............., (a+b)a
2
= ..............,
(a+b) b
2
= .............., a
2
b = .............., ab
2
= ..............,
ab (a+b)
= ..............,
Therefore, a
3
+ b
3
= (a + b) (a
2
+ b
2
– ab).
APPLICATION
The identity may be used in simplification and factorisation of algebraic
expressions.
Fig. 6
14/04/18
Mathematics 35
METHOD OF CONSTRUCTION
1. Make a cuboid of dimensions (a–b) × a × a (b < a), using acrylic sheet and
cellotape/adhesive as shown in Fig. 1.
2. Make another cuboid of dimensions (a–b) × a × b, using acrylic sheet and
cellotape/adhesive as shown in Fig. 2.
3. Make one more cuboid of dimensions (a–b) × b × b as shown in Fig. 3.
4. Make a cube of dimensions b × b × b using acrylic sheet as shown in Fig. 4.
OBJECTIVE
MATERIAL REQUIRED
To verify the algebraic identity :
a
3
– b
3
= (a – b)(a
2
+ ab + b
2
)
Acrylic sheet, sketch pen, glazed
papers, scissors, adhesive, cello-
tape, coloured papers, cutter.
Activity 10
Fig. 1
Fig. 2
Fig. 3
Fig. 4
14/04/18
36
Laboratory Manual
5. Arrange the cubes and cuboids made above in Steps (1), (2), (3) and (4) to
obtain a solid as shown in Fig. 5, which is a cube of volume a
3
cubic units.
DEMONSTRATION
Volume of cuboid in Fig. 1 = (a–b) × a × a cubic units.
Volume of cuboid in Fig. 2 = (a–b) × a × b cubic units.
Volume of cuboid in Fig. 3 = (a–b) × b × b cubic units.
Volume of cube in Fig. 4 = b
3
cubic units.
Volume of solid in Fig. 5 = a
3
cubic units.
Removing a cube of size b
3
cubic units from the solid in Fig. 5, we obtain a solid
as shown in Fig. 6.
Volume of solid in Fig. 6 = (a–b) a
2
+ (a–b) ab + (a–b) b
2
= (a–b) (a
2
+ ab + b
2
)
Therefore, a
3
– b
3
= (a – b)(a
2
+ ab + b
2
)
Fig. 5
Fig. 6
14/04/18

Mathematics 37
OBSERVATION
On actual measurement:
a = .............., b = ..............,
So, a
3
=
.............., b
3
= .............., (a–b) = .............., ab = ..............,
a
2
= .............., b
2
= ..............,
Therefore, a
3
– b
3
= (a – b) (a
2
+ ab + b
2
).
APPLICATION
The identity may be used in simplification/factorisation of algebraic expressions.
14/04/18
